The customer service team is always listening, taking notes, and quantifying complaints to ensure our products are continually improved. Due to selling directly to you, the customer, via Amazon, we can use product reviews to help us improve our existing products or help further development of new products.
The Effects of Low Humidity and How to Deal with It
Table of Contents
Did you know that dry hair can damage your skin, eyes, and even respiratory tract? If you have been feeling sick lately, then it could simply be that you have decreased humidity in your home. With seasons changing, it can often be the dip in water vapor that causes you to feel like you have a cold.
If you have certain breathing conditions, decreased humidity can cause even more damage. Studies have shown that relative humidity in indoor environments may spark respiratory illnesses and other problems due to allergens.
Winter Home Moisture Problems
When the winter season rolls around, there are additional precautions that you should take to maintain the humidity level. This also depends on where you live and what type of windows you have in your home. The Pacific Northwest also trends towards being more humid during the winter due to wet weather.
Some of the signs for high humidity levels in your home could be condensation on the windows, a muggy feeling, musty odors, and allergy symptoms. For decreased humidity, heaters and colder weather lead to dry air, which causes dry skin, sore throats, irritated sinuses, and itchy eyes.
This is especially true if you like to keep your house warmer in cold months, thereby running the heater more often. You’ll need to use a thermometer or humidifier to help fix these issues.
What is Relative Humidity
Humidity refers to water vapor in the air. Levels of humidity can be extreme, whether high or low, in which case they cause different health problems. However, low and high humidity levels are often unchecked, leading to indoor health problems that may resemble a cold, cough, allergies, or other respiratory illnesses. In the case of too much humidity, your home might show signs of fungus, mold, and dust mites, which can taint the air quality even further.
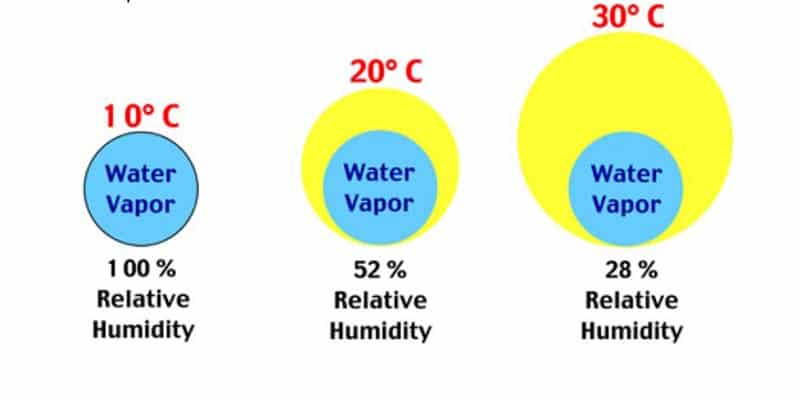
Relative humidity levels should remain between 40 and 60 percent to ensure good air quality. The best way to do this is with a hygrometer, but there are other ways to note whether your home is susceptible to humidity problems.
What are the Effects of Low Humidity
The amount of water vapor in the air can directly relate to poor sinus health. Ideal humidity levels maintain the right moisture in the air, allowing your sinuses to breath and keeping allergens at bay. Exposure to decreased humidity can cause severe respiratory problems. During the winter months, you may experience dry skin, irritated sinuses, red and sore eyes, and problems with your respiratory tract. This is due to the low moisture in the eye, which can inflame the mucous membrane that lines your respiratory tract. Since this membrane is very sensitive, it can lead to more problems and increased risk of infection. This includes a risk to incur a cold or the flu. Since the flu virus can survive longer with decreased humidity, it can also spread faster as well.
Nasal congestion is a prime example of what happens in decreased humidity. The interaction between the moisture and temperature can cause nasal cooling, which affects the air as it moves through your nasal cavity. The sensors in your nose can sense cooler, dryer air, which can trigger congestion, sneezing, and other problems.
If you struggle with irritated, itchy eyes, then lower humidity could be a problem. You will typically experience an increase in watery eyes, disrupting the moisture balance for a more comfortable surface.
With cold temperatures in play, your skin will become scaly, itchy, and dry, resembling eczema. While lotion can help, paying attention to the humidity levels in your home can diminish the dry air effect on your skin. This is also called “winter itch,” when your skin loses moisture due to the colder season and dry air. You may start to see small cracks on your skin’s surface.
When it’s rare for skin infections to occur because of dry skin, there have been instances where cracked skin can become so severe that you risk getting sick and dangerous pathogens can get into your skin.
If you notice that humidity levels drop below 10 percent in your home, then the dry environment will create most of these problems and aggravate other issues, such as allergies.
Effects on Your Home’s Structure and Furniture
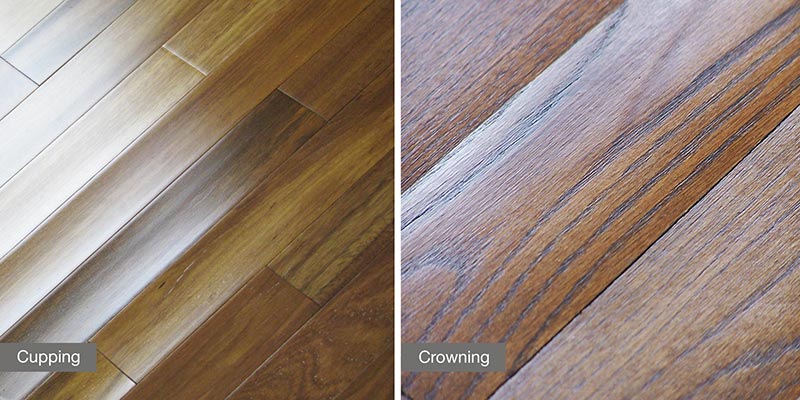

Decreased humidity can cause more damage than health issues. You may notice that your houseplants are drying out and dying. Wallpaper may peel at the seams and edges. There will also be an increase in static electricity.
Decreased humidity can also cause problems for hardwood floors, such as cracks and separate at the seams. While most people focus on winter seasons causing dry air, there are areas where dry, arid summer seasons can also cause issues due to excessive air conditioning.
When this happens, you’ll notice that your wood furniture can crack or become damaged if dry air persists for longer than a couple of weeks.
What is Ideal Humidity
Most studies place ideal relative humidity in your home between 40 and 60 percent. However, this can change during certain seasons. For example, in the winter, your relative humidity levels could be lower than 40% RH to avoid issues with condensation on the windows.
How to Check Humidity
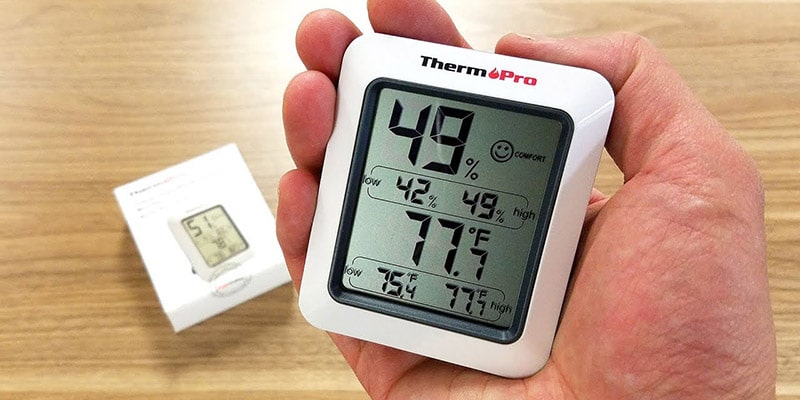

One of the best things to use is a ThermoPro indoor thermometer. These thermometers can monitor temperatures and humidity percentages, alerting you to low and high humidity percentages. You can set humidity ranges between 10 and 90 percent, as well as track humidity levels from 200 feet away.
If you have access to a hygrometer, you can check your humidity levels with just a press of a button. These are most often used by meteorologists to test the water vapor in the air. However, electrical hygrometers are now available to the public and can be purchased online.
There are other ways to note whether your humidity levels are high or low. For example, if the windows in your home are constantly fogging up, creating condensation and mold on the edges of your windows, then you have a house with high indoor humidity.
There’s another test you can do with a glass of water and three ice cubes. First, make the ice water and then set it in the middle of your living room for three minutes. If moisture doesn’t form on the outside of the glass, then the air is too dry. This indicates you could use a humidifier in your home.
How to Deal with Low Humidity Problems
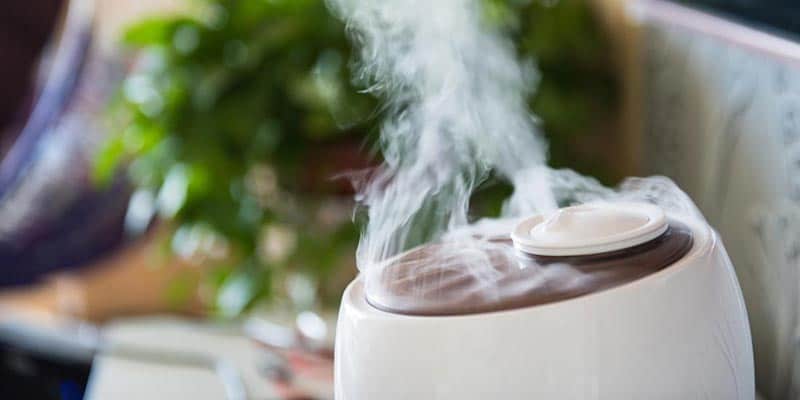

For homes with decreased humidity problems, some household appliances can help increase the moisture in your air. However, you’ll still need a ThermoPro indoor thermometer or another measurement to ensure that your humidity levels are set appropriately.
There are a few differences between vaporizers and humidifiers that will make a difference if you have certain health conditioners.
Humidifiers increase the moisture content in a surrounding square footage. During the winter, people with dry homes use humidifiers to add moisture back into the air. The process is different from a vaporizer because it creates water vapor using a quick turning disk that is submerged in water within the appliance.
Since there’s no heating involved, humidifiers are a bit safer than vaporizers, which do use heat. However, it also emits cold vapors. There are a few risks with bacteria problems for humidifiers if you do not properly maintain and clean the filters.
Vaporizers are used to take in extracts of plants or other sources for cold and health benefits. These appliances focus on plant essences and herbs, creating moisture for inhalation. The heating element in a vaporizer creates the steam, which can cause serious injury if touched. There isn’t any risk of bacteria as there is with a humidifier, however.
Most homeowners with dry homes will prefer a humidifier since it’s made to deal with dry hair. However, if you have bacteria-related problems or are prone to respiratory problems, then a vaporizer may be a better option as you can inhale the steam to break up congestion.
You can also take steam baths or hot showers, increasing steam the hotter you turn the water. If you have congestion from dry hair, you can also fill your sink with hot water and place a towel over your head as you lead down to inhale.
Another way people increase moisture in their homes is by boiling water on their stoves or placing hot bowls of water around the house.
Humidifier Warning
With a humidifier, you do need to be careful that you don’t cause too much moisture in the air, which can lead to more significant health problems. High humidity levels can cause mold to grow, which will be devastating to your health.
Additionally, the warm environments of a humidifier will create more bacteria and fungi, which will travel out of the humidifier as a toxic mist. If you notice a change in the air quality and your home starts to smell musky or feel muggy, then chances are you have a real high humidity level. You can use a thermometer to check that it remains between 40 and 60 percent.
For how to deal with high humidity, please check out this post: How to Reduce Home Humidity during Rainy Spring
Conclusion
If someone in your home continues to sneeze or have congestion, then you should check your humidity levels to ensure that the humidity levels aren’t too high or low. The ideal indoor humidity level should remain between 40 and 60 percent typically, but this can change depending on the season. For example, in colder, winter months, the air tends to be dryer, in which case you may want to increase humidity levels with a humidifier.









